Introduction: Why Turbidity Monitoring is Critical
Turbidity, a key indicator of water quality, measures the cloudiness caused by suspended particles. Effective turbidity monitoring is non-negotiable for ensuring safe drinking water, optimizing wastewater treatment processes, and complying with environmental regulations. For applications requiring high precision in clean or lightly polluted water, a low-range turbidity sensor is the ideal tool.
This guide explores how these advanced optical sensors work and what to look for when integrating one into your water quality monitoring system.
What is a Low-Range Turbidity Sensor?
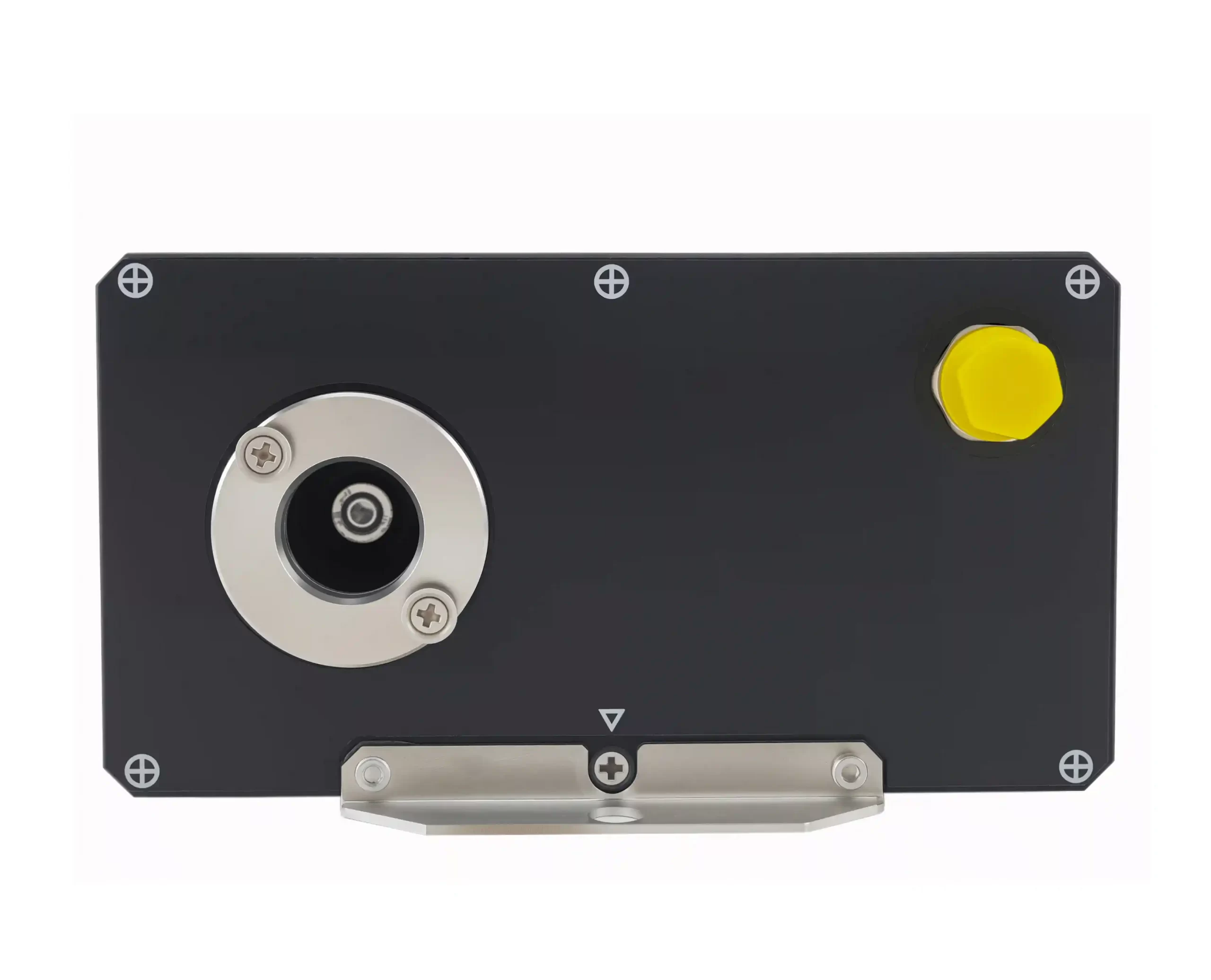
A low-range turbidity sensor is an optical instrument designed to detect minute levels of suspended solids in water, typically for measurements below 1 NTU (Nephelometric Turbidity Unit). Unlike general-purpose sensors, they are engineered for high sensitivity and stability in applications where even slight changes in water clarity are critical.
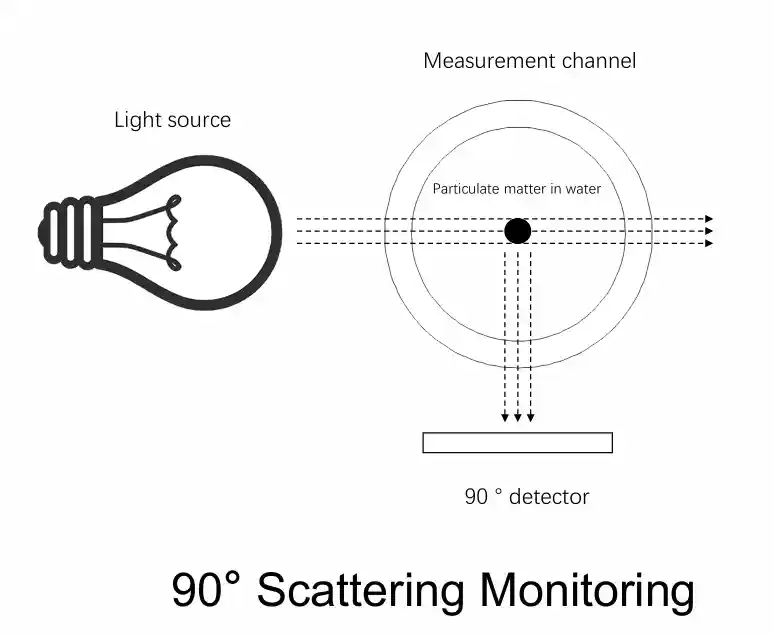
Our SPECSENS SPS-T-SC3 turbidity sensor, for instance, uses a sophisticated 90° scattered light principle to deliver reliable data with minimal maintenance.
How a Turbidity Sensor Works: Scattered Light & Ratiometric Analysis
Understanding the technology behind the sensor is key to appreciating its accuracy. Most modern water turbidity sensors use one of two optical methods:
- Scattering Method (Nephelometry): This method, endorsed by the ISO 7027 standard, involves projecting a light beam into the water and measuring the light scattered at a 90-degree angle by suspended particles. It is highly reliable and less influenced by particle size.
- Transmission Method: This measures the attenuation of light as it passes through the water sample.
To overcome challenges like variable light source intensity and color interference, advanced sensors like ours use a ratiometric method. This technique compares the intensity of the 90° scattered light to the transmitted light, resulting in a more stable and accurate measurement that requires less frequent calibration.
Key Features of an Industrial-Grade Turbidity Sensor
When selecting a sensor for industrial or municipal use, consider these essential features:
- High Accuracy & Low Range: Capable of detecting changes as small as 0.015 NTU.
- Self-Cleaning Mechanism: Reduces fouling and maintenance, enabling 1-3 months of unattended operation.
- Robust Communication: RS485 interface for seamless integration into SCADA or PLC-based control systems.
- Durable Design: Built to withstand pressures up to 1 MPa for immersion in deep tanks or pipelines.
Where Are Low-Range Turbidity Sensors Used?
This technology is versatile and critical across numerous sectors:
- Drinking Water Treatment: Monitoring filter effluent and final water quality.
- Wastewater Treatment Plants: Optimizing chemical dosing and monitoring clarifier effluent.
- Industrial Processes: Controlling water purity in pharmaceutical, food, and beverage production.
- Environmental Monitoring: Tracking sediment levels in rivers, lakes, and discharge water.
Compliance and Standards: ISO 7027 and Formazin Calibration
For regulatory compliance, it is crucial to choose a sensor that adheres to international standards. Our sensors are ISO 7027 compliant, ensuring the measurement method is recognized and respected globally. They are calibrated using Formazin standard solutions, the primary reference for turbidity calibration, guaranteeing traceable and accurate results.
Choosing the Right Turbidity Sensor for Your Application
Selecting the best sensor depends on your specific needs. Here’s a quick checklist:
- Confirm the Measurement Range: Ensure the sensor covers your typical operating NTU levels.
- Verify Accuracy Needs: For process control or compliance, high accuracy is a must.
- Evaluate Maintenance Requirements: Opt for sensors with self-cleaning features to lower lifecycle costs.
- Check Compliance: Look for ISO 7027 compliance for universally accepted data.
- Assess Integration: Confirm the communication protocol (e.g., RS485) works with your existing system.
Conclusion: Invest in Precision and Reliability
A high-performance specsens SPS-T-SC3 low-range turbidity sensor is more than an instrument—it’s your first line of defence in ensuring water quality, process efficiency, and regulatory compliance. By investing in a robust, accurate, and low-maintenance sensor, you secure a foundation for reliable and actionable water quality data.

